SpringSecurity学习 简介 Spring Security 是 Spring 家族中的一个安全管理框架。相比与另外一个安全框架 Shiro ,它提供了更丰富的功能,社区资源也比 Shiro 丰富。
一般来说中大型的项目都是使用 SpringSecurity 来做安全框架。小项目有 Shiro 的比较多,因为相比与 SpringSecurity,Shiro 的上手更加的简单。
一般 Web 应用的需要进行认证 和授权 。
认证:验证当前访问系统的是不是本系统的用户,并且要确认具体是哪个用户
授权:经过认证后判断当前用户是否有权限进行某个操作
而认证和授权也是 SpringSecurity 作为安全框架的核心功能。
1. 快速入门 1.1 准备工作 我们先要搭建一个简单的 SpringBoot 工程
① 设置父工程 添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <parent>2.5 .0 </version>true </optional>
② 创建启动类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication public class SecurityApplication {public static void main (String[] args) {
③ 创建 Controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController public class HelloController {@RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello () {return "hello" ;
1.2 引入 SpringSecurity 在 SpringBoot 项目中使用 SpringSecurity 我们只需要引入依赖即可实现入门案例。
1 2 3 4 <dependency>
引入依赖后我们在尝试去访问之前的接口就会自动跳转到一个 SpringSecurity 的默认登陆页面,默认用户名是 user, 密码会输出在控制台。
必须登陆之后才能对接口进行访问。
2. 认证 2.1 登陆校验流程
2.2 原理初探 想要知道如何实现自己的登陆流程就必须要先知道入门案例中 SpringSecurity 的流程。
2.2.1 SpringSecurity 完整流程
SpringSecurity 的原理其实就是一个过滤器链,内部包含了提供各种功能的过滤器。这里我们可以看看入门案例中的过滤器。
图中只展示了核心过滤器,其它的非核心过滤器并没有在图中展示。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter : 负责处理我们在登陆页面填写了用户名密码后的登陆请求。入门案例的认证工作主要有它负责。
ExceptionTranslationFilter: 处理过滤器链中抛出的任何 AccessDeniedException 和 AuthenticationException 。
FilterSecurityInterceptor: 负责权限校验的过滤器。
我们可以通过 Debug 查看当前系统中 SpringSecurity 过滤器链中有哪些过滤器及它们的顺序。
2.2.2 认证流程详解
概念速查:
Authentication 接口: 它的实现类,表示当前访问系统的用户,封装了用户相关信息。
AuthenticationManager 接口:定义了认证 Authentication 的方法
UserDetailsService 接口:加载用户特定数据的核心接口。里面定义了一个根据用户名查询用户信息的方法。
UserDetails 接口:提供核心用户信息。通过 UserDetailsService 根据用户名获取处理的用户信息要封装成 UserDetails 对象返回。然后将这些信息封装到 Authentication 对象中。
2.3 解决问题 2.3.1 思路分析
登录
①自定义登录接口
调用 ProviderManager 的方法进行认证 如果认证通过生成 jwt
把用户信息存入 redis 中
②自定义 UserDetailsService
在这个实现类中去查询数据库
校验:
①定义 Jwt 认证过滤器
获取 token
解析 token 获取其中的 userid
从 redis 中获取用户信息
存入 SecurityContextHolder
2.3.2 准备工作
①添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <!--redis依赖-->1.2 .33 </version>0.9 .0 </version>
② 添加 Redis 相关配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JavaType;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.type.TypeFactory;import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.SerializationException;import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig;import org.springframework.util.Assert;import java.nio.charset.Charset;public class FastJsonRedisSerializer <T> implements RedisSerializer <T>public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8" );private Class<T> clazz;static true );public FastJsonRedisSerializer (Class<T> clazz) super ();this .clazz = clazz;@Override public byte [] serialize(T t) throws SerializationExceptionif (t == null )return new byte [0 ];return JSON.toJSONString(t, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName).getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET);@Override public T deserialize (byte [] bytes) throws SerializationExceptionif (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0 )return null ;String str = new String (bytes, DEFAULT_CHARSET);return JSON.parseObject(str, clazz);protected JavaType getJavaType (Class<?> clazz) return TypeFactory.defaultInstance().constructType(clazz);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;@Configuration public class RedisConfig {@Bean @SuppressWarnings(value = { "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate (RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) new RedisTemplate <>();FastJsonRedisSerializer serializer = new FastJsonRedisSerializer (Object.class);new StringRedisSerializer ());new StringRedisSerializer ());return template;
③ 响应类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL) public class ResponseResult <T> {private Integer code;private String msg;private T data;public ResponseResult (Integer code, String msg) {this .code = code;this .msg = msg;public ResponseResult (Integer code, T data) {this .code = code;this .data = data;public Integer getCode () {return code;public void setCode (Integer code) {this .code = code;public String getMsg () {return msg;public void setMsg (String msg) {this .msg = msg;public T getData () {return data;public void setData (T data) {this .data = data;public ResponseResult (Integer code, String msg, T data) {this .code = code;this .msg = msg;this .data = data;
④工具类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;import io.jsonwebtoken.JwtBuilder;import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;import javax.crypto.SecretKey;import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.Date;import java.util.UUID;public class JwtUtil {public static final Long JWT_TTL = 60 * 60 *1000L ;public static final String JWT_KEY = "zty" ;public static String getUUID () {String token = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-" , "" );return token;public static String createJWT (String subject) {JwtBuilder builder = getJwtBuilder(subject, null , getUUID());return builder.compact();public static String createJWT (String subject, Long ttlMillis) {JwtBuilder builder = getJwtBuilder(subject, ttlMillis, getUUID());return builder.compact();private static JwtBuilder getJwtBuilder (String subject, Long ttlMillis, String uuid) {SignatureAlgorithm signatureAlgorithm = SignatureAlgorithm.HS256;SecretKey secretKey = generalKey();long nowMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();Date now = new Date (nowMillis);if (ttlMillis==null ){long expMillis = nowMillis + ttlMillis;Date expDate = new Date (expMillis);return Jwts.builder()"sg" ) public static String createJWT (String id, String subject, Long ttlMillis) {JwtBuilder builder = getJwtBuilder(subject, ttlMillis, id);return builder.compact();public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {String token = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJjYWM2ZDVhZi1mNjVlLTQ0MDAtYjcxMi0zYWEwOGIyOTIwYjQiLCJzdWIiOiJzZyIsImlzcyI6InNnIiwiaWF0IjoxNjM4MTA2NzEyLCJleHAiOjE2MzgxMTAzMTJ9.JVsSbkP94wuczb4QryQbAke3ysBDIL5ou8fWsbt_ebg" ;Claims claims = parseJWT(token);public static SecretKey generalKey () {byte [] encodedKey = Base64.getDecoder().decode(JwtUtil.JWT_KEY);SecretKey key = new SecretKeySpec (encodedKey, 0 , encodedKey.length, "AES" );return key;public static Claims parseJWT (String jwt) throws Exception {SecretKey secretKey = generalKey();return Jwts.parser()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 import java.util.*;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@SuppressWarnings(value = { "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) @Component public class RedisCache @Autowired public RedisTemplate redisTemplate;public <T> void setCacheObject (final String key, final T value) public <T> void setCacheObject (final String key, final T value, final Integer timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit) public boolean expire (final String key, final long timeout) return expire(key, timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS);public boolean expire (final String key, final long timeout, final TimeUnit unit) return redisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit);public <T> T getCacheObject (final String key) return operation.get(key);public boolean deleteObject (final String key) return redisTemplate.delete(key);public long deleteObject (final Collection collection) return redisTemplate.delete(collection);public <T> long setCacheList (final String key, final List<T> dataList) Long count = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, dataList);return count == null ? 0 : count;public <T> List<T> getCacheList (final String key) return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, 0 , -1 );public <T> BoundSetOperations<String, T> setCacheSet (final String key, final Set<T> dataSet) while (it.hasNext())return setOperation;public <T> Set<T> getCacheSet (final String key) return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);public <T> void setCacheMap (final String key, final Map<String, T> dataMap) if (dataMap != null ) {public <T> Map<String, T> getCacheMap (final String key) return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);public <T> void setCacheMapValue (final String key, final String hKey, final T value) public <T> T getCacheMapValue (final String key, final String hKey) return opsForHash.get(key, hKey);public void delCacheMapValue (final String key, final String hkey) HashOperations hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();public <T> List<T> getMultiCacheMapValue (final String key, final Collection<Object> hKeys) return redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, hKeys);public Collection<String> keys (final String pattern) return redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;public class WebUtils public static String renderString (HttpServletResponse response, String string) {try 200 );"application/json" );"utf-8" );catch (IOException e)return null ;
⑤实体类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Date;@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class User implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -40356785423868312L ;private Long id;private String userName;private String nickName;private String password;private String status;private String email;private String phonenumber;private String sex;private String avatar;private String userType;private Long createBy;private Date createTime;private Long updateBy;private Date updateTime;private Integer delFlag;
2.3.3 实现 2.3.3.1 数据库校验用户 从之前的分析我们可以知道,我们可以自定义一个 UserDetailsService, 让 SpringSecurity 使用我们的 UserDetailsService。我们自己的 UserDetailsService 可以从数据库中查询用户名和密码。
准备工作
我们先创建一个用户表, 建表语句如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 CREATE TABLE `sys_user` (
引入 MybatisPuls 和 mysql 驱动的依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <dependency>3.4 .3 </version>
配置数据库信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 spring:
定义 Mapper 接口
1 2 public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper <User> {
修改 User 实体类
1 类名上加@TableName(value = "sys_user") ,id字段上加 @TableId
配置 Mapper 扫描
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.zty.mapper") public class SimpleSecurityApplication {public static void main (String[] args) {ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(SimpleSecurityApplication.class);
添加 junit 依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency>
测试 MP 是否能正常使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @SpringBootTest public class MapperTest {@Autowired private UserMapper userMapper;@Test public void testUserMapper () {null );
核心代码实现
创建一个类实现 UserDetailsService 接口,重写其中的方法。更加用户名从数据库中查询用户信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @Service public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {@Autowired private UserMapper userMapper;@Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername (String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {new LambdaQueryWrapper <>();User user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);if (Objects.isNull(user)){throw new RuntimeException ("用户名或密码错误" );return new LoginUser (user);
因为 UserDetailsService 方法的返回值是 UserDetails 类型,所以需要定义一个类,实现该接口,把用户信息封装在其中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class LoginUser implements UserDetails {private User user;@Override public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority > getAuthorities() {return null ;@Override public String getPassword () {return user.getPassword();@Override public String getUsername () {return user.getUserName();@Override public boolean isAccountNonExpired () {return true ;@Override public boolean isAccountNonLocked () {return true ;@Override public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired () {return true ;@Override public boolean isEnabled () {return true ;
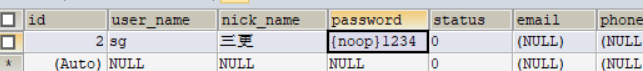
注意:如果要测试,需要往用户表中写入用户数据,并且如果你想让用户的密码是明文存储,需要在密码前加 {noop}。例如
这样登陆的时候就可以用 sg 作为用户名,1234 作为密码来登陆了。
2.3.3.2 密码加密存储
实际项目中我们不会把密码明文存储在数据库中。
默认使用的 PasswordEncoder 要求数据库中的密码格式为:{id}password 。它会根据 id 去判断密码的加密方式。但是我们一般不会采用这种方式。所以就需要替换 PasswordEncoder。
我们一般使用 SpringSecurity 为我们提供的 BCryptPasswordEncoder。
我们只需要使用把 BCryptPasswordEncoder 对象注入 Spring 容器中,SpringSecurity 就会使用该 PasswordEncoder 来进行密码校验。
我们可以定义一个 SpringSecurity 的配置类,SpringSecurity 要求这个配置类要继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder () {return new BCryptPasswordEncoder ();
2.3.3.3 登陆接口 接下我们需要自定义登陆接口,然后让 SpringSecurity 对这个接口放行, 让用户访问这个接口的时候不用登录也能访问。
在接口中我们通过 AuthenticationManager 的 authenticate 方法来进行用户认证, 所以需要在 SecurityConfig 中配置把 AuthenticationManager 注入容器。
认证成功的话要生成一个 jwt,放入响应中返回。并且为了让用户下回请求时能通过 jwt 识别出具体的是哪个用户,我们需要把用户信息存入 redis,可以把用户 id 作为 key。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @RestController public class LoginController {@Autowired private LoginServcie loginServcie;@PostMapping("/user/login") public ResponseResult login (@RequestBody User user) {return loginServcie.login(user);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder () {return new BCryptPasswordEncoder ();@Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {"/user/login" ).anonymous()@Bean @Override public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean () throws Exception {return super .authenticationManagerBean();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @Service public class LoginServiceImpl implements LoginServcie {@Autowired private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;@Autowired private RedisCache redisCache;@Override public ResponseResult login (User user) {UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken (user.getUserName(),user.getPassword());Authentication authenticate = authenticationManager.authenticate(authenticationToken);if (Objects.isNull(authenticate)){throw new RuntimeException ("用户名或密码错误" );LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authenticate.getPrincipal();String userId = loginUser.getUser().getId().toString();String jwt = JwtUtil.createJWT(userId);"login:" +userId,loginUser);new HashMap <>();"token" ,jwt);return new ResponseResult (200 ,"登陆成功" ,map);
2.3.3.4 认证过滤器
我们需要自定义一个过滤器,这个过滤器会去获取请求头中的 token,对 token 进行解析取出其中的 userid。
使用 userid 去 redis 中获取对应的 LoginUser 对象。
然后封装 Authentication 对象存入 SecurityContextHolder
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 @Component public class JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {@Autowired private RedisCache redisCache;@Override protected void doFilterInternal (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {String token = request.getHeader("token" );if (!StringUtils.hasText(token)) {return ;try {Claims claims = JwtUtil.parseJWT(token);catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException ("token非法" );String redisKey = "login:" + userid;LoginUser loginUser = redisCache.getCacheObject(redisKey);if (Objects.isNull(loginUser)){throw new RuntimeException ("用户未登录" );UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken (loginUser,null ,null );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder () {return new BCryptPasswordEncoder ();@Autowired @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {"/user/login" ).anonymous()@Bean @Override public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean () throws Exception {return super .authenticationManagerBean();
2.3.3.5 退出登陆
我们只需要定义一个登陆接口,然后获取 SecurityContextHolder 中的认证信息,删除 redis 中对应的数据即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 @Service public class LoginServiceImpl implements LoginServcie {@Autowired private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;@Autowired private RedisCache redisCache;@Override public ResponseResult login (User user) {UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken (user.getUserName(),user.getPassword());Authentication authenticate = authenticationManager.authenticate(authenticationToken);if (Objects.isNull(authenticate)){throw new RuntimeException ("用户名或密码错误" );LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authenticate.getPrincipal();String userId = loginUser.getUser().getId().toString();String jwt = JwtUtil.createJWT(userId);"login:" +userId,loginUser);new HashMap <>();"token" ,jwt);return new ResponseResult (200 ,"登陆成功" ,map);@Override public ResponseResult logout () {Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authentication.getPrincipal();Long userid = loginUser.getUser().getId();"login:" +userid);return new ResponseResult (200 ,"退出成功" );
3. 授权 3.0 权限系统的作用 例如一个学校图书馆的管理系统,如果是普通学生登录就能看到借书还书相关的功能,不可能让他看到并且去使用添加书籍信息,删除书籍信息等功能。但是如果是一个图书馆管理员的账号登录了,应该就能看到并使用添加书籍信息,删除书籍信息等功能。
总结起来就是不同的用户可以使用不同的功能 。这就是权限系统要去实现的效果。
我们不能只依赖前端去判断用户的权限来选择显示哪些菜单哪些按钮。因为如果只是这样,如果有人知道了对应功能的接口地址就可以不通过前端,直接去发送请求来实现相关功能操作。
所以我们还需要在后台进行用户权限的判断,判断当前用户是否有相应的权限,必须具有所需权限才能进行相应的操作。
3.1 授权基本流程 在 SpringSecurity 中,会使用默认的 FilterSecurityInterceptor 来进行权限校验。在 FilterSecurityInterceptor 中会从 SecurityContextHolder 获取其中的 Authentication,然后获取其中的权限信息。当前用户是否拥有访问当前资源所需的权限。
所以我们在项目中只需要把当前登录用户的权限信息也存入 Authentication。
然后设置我们的资源所需要的权限即可。
3.2 授权实现 3.2.1 限制访问资源所需权限
SpringSecurity 为我们提供了基于注解的权限控制方案,这也是我们项目中主要采用的方式。我们可以使用注解去指定访问对应的资源所需的权限。
但是要使用它我们需要先开启相关配置。
1 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
然后就可以使用对应的注解。@PreAuthorize
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @RestController public class HelloController {@RequestMapping("/hello") @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('test')") public String hello () {return "hello" ;
3.2.2 封装权限信息
我们前面在写 UserDetailsServiceImpl 的时候说过,在查询出用户后还要获取对应的权限信息,封装到 UserDetails 中返回。
我们先直接把权限信息写死封装到 UserDetails 中进行测试。
我们之前定义了 UserDetails 的实现类 LoginUser,想要让其能封装权限信息就要对其进行修改。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 package com.zty.domain;import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.List;import java.util.stream.Collectors;@Data @NoArgsConstructor public class LoginUser implements UserDetails {private User user;private List<String> permissions;public LoginUser (User user,List<String> permissions) {this .user = user;this .permissions = permissions;@JSONField(serialize = false) private List<GrantedAuthority> authorities;@Override public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority > getAuthorities() {if (authorities!=null ){return authorities;new )return authorities;@Override public String getPassword () {return user.getPassword();@Override public String getUsername () {return user.getUserName();@Override public boolean isAccountNonExpired () {return true ;@Override public boolean isAccountNonLocked () {return true ;@Override public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired () {return true ;@Override public boolean isEnabled () {return true ;
LoginUser 修改完后我们就可以在 UserDetailsServiceImpl 中去把权限信息封装到 LoginUser 中了。我们写死权限进行测试,后面我们再从数据库中查询权限信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 package com.zty.service.impl;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.conditions.query.LambdaQueryChainWrapper;import com.zty.domain.LoginUser;import com.zty.domain.User;import com.zty.mapper.UserMapper;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.List;import java.util.Objects;@Service public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {@Autowired private UserMapper userMapper;@Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername (String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {new LambdaQueryWrapper <>();User user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);if (Objects.isNull(user)){throw new RuntimeException ("用户名或密码错误" );new ArrayList <>(Arrays.asList("test" ));return new LoginUser (user,list);
3.2.3 从数据库查询权限信息
3.2.3.1 RBAC 权限模型
RBAC 权限模型(Role-Based Access Control)即:基于角色的权限控制。这是目前最常被开发者使用也是相对易用、通用权限模型。
3.2.3.2 准备工作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`sg_security` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 */;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 SELECT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 package com.zty.domain;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Date;@TableName(value="sys_menu") @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL) public class Menu implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -54979041104113736L ;@TableId private Long id;private String menuName;private String path;private String component;private String visible;private String status;private String perms;private String icon;private Long createBy;private Date createTime;private Long updateBy;private Date updateTime;private Integer delFlag;private String remark;
3.2.3.3 代码实现
我们只需要根据用户 id 去查询到其所对应的权限信息即可。
所以我们可以先定义个 mapper,其中提供一个方法可以根据 userid 查询权限信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;import com.zty.domain.Menu;import java.util.List;public interface MenuMapper extends BaseMapper <Menu> {selectPermsByUserId (Long id) ;
尤其是自定义方法,所以需要创建对应的 mapper 文件,定义对应的 sql 语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>"-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >"com.zty.mapper.MenuMapper" >"selectPermsByUserId" resultType="java.lang.String" >WHERE user_id = #{userid}0 0
在 application.yml 中配置 mapperXML 文件的位置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 spring:6379
然后我们可以在 UserDetailsServiceImpl 中去调用该 mapper 的方法查询权限信息封装到 LoginUser 对象中即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Service public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {@Autowired private UserMapper userMapper;@Autowired private MenuMapper menuMapper;@Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername (String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {new LambdaQueryWrapper <>();User user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);if (Objects.isNull(user)){throw new RuntimeException ("用户名或密码错误" );return new LoginUser (user,permissionKeyList);
4. 自定义失败处理 我们还希望在认证失败或者是授权失败的情况下也能和我们的接口一样返回相同结构的 json,这样可以让前端能对响应进行统一的处理。要实现这个功能我们需要知道 SpringSecurity 的异常处理机制。
在 SpringSecurity 中,如果我们在认证或者授权的过程中出现了异常会被 ExceptionTranslationFilter 捕获到。在 ExceptionTranslationFilter 中会去判断是认证失败还是授权失败出现的异常。
如果是认证过程中出现的异常会被封装成 AuthenticationException 然后调用 AuthenticationEntryPoint 对象的方法去进行异常处理。
如果是授权过程中出现的异常会被封装成 AccessDeniedException 然后调用 AccessDeniedHandler 对象的方法去进行异常处理。
所以如果我们需要自定义异常处理,我们只需要自定义 AuthenticationEntryPoint 和 AccessDeniedHandler 然后配置给 SpringSecurity 即可。
①自定义实现类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Component public class AccessDeniedHandlerImpl implements AccessDeniedHandler {@Override public void handle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult (HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value(), "权限不足" );String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Component public class AuthenticationEntryPointImpl implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {@Override public void commence (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult (HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(), "认证失败请重新登录" );String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);
②配置给 SpringSecurity
先注入对应的处理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Autowired private AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;@Autowired private AccessDeniedHandler accessDeniedHandler;
5. 跨域 浏览器出于安全的考虑,使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象发起 HTTP 请求时必须遵守同源策略,否则就是跨域的 HTTP 请求,默认情况下是被禁止的。 同源策略要求源相同才能正常进行通信,即协议、域名、端口号都完全一致。
前后端分离项目,前端项目和后端项目一般都不是同源的,所以肯定会存在跨域请求的问题。
所以我们就要处理一下,让前端能进行跨域请求。
①先对 SpringBoot 配置,运行跨域请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Configuration public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Override public void addCorsMappings (CorsRegistry registry) {"/**" )"*" )true )"GET" , "POST" , "DELETE" , "PUT" )"*" )3600 );
②开启 SpringSecurity 的跨域访问
由于我们的资源都会收到 SpringSecurity 的保护,所以想要跨域访问还要让 SpringSecurity 运行跨域访问。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {"/user/login" ).anonymous()
6. 遗留小问题 其它权限校验方法 我们前面都是使用 @PreAuthorize 注解,然后在在其中使用的是 hasAuthority 方法进行校验。SpringSecurity 还为我们提供了其它方法例如:hasAnyAuthority,hasRole,hasAnyRole 等。
这里我们先不急着去介绍这些方法,我们先去理解 hasAuthority 的原理,然后再去学习其他方法你就更容易理解,而不是死记硬背区别。并且我们也可以选择定义校验方法,实现我们自己的校验逻辑。
hasAuthority 方法实际是执行到了 SecurityExpressionRoot 的 hasAuthority,大家只要断点调试既可知道它内部的校验原理。
它内部其实是调用 authentication 的 getAuthorities 方法获取用户的权限列表。然后判断我们存入的方法参数数据在权限列表中。
hasAnyAuthority 方法可以传入多个权限,只有用户有其中任意一个权限都可以访问对应资源。
1 2 3 4 @PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin','test','system:dept:list')") public String hello () {return "hello" ;
hasRole 要求有对应的角色才可以访问,但是它内部会把我们传入的参数拼接上 ROLE_ 后再去比较。所以这种情况下要用用户对应的权限也要有 ROLE_ 这个前缀才可以。
1 2 3 4 @PreAuthorize("hasRole('system:dept:list')") public String hello () {return "hello" ;
hasAnyRole 有任意的角色就可以访问。它内部也会把我们传入的参数拼接上 ROLE_ 后再去比较。所以这种情况下要用用户对应的权限也要有 ROLE_ 这个前缀才可以。
1 2 3 4 @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('admin','system:dept:list')") public String hello () {return "hello" ;
自定义权限校验方法 我们也可以定义自己的权限校验方法,在 @PreAuthorize 注解中使用我们的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Component("ex") public class SGExpressionRoot {public boolean hasAuthority (String authority) {Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authentication.getPrincipal();return permissions.contains(authority);
在 SPEL 表达式中使用 @ex 相当于获取容器中 bean 的名字未 ex 的对象。然后再调用这个对象的 hasAuthority 方法
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/hello") @PreAuthorize("@ex.hasAuthority('system:dept:list')") public String hello () {return "hello" ;
基于配置的权限控制 我们也可以在配置类中使用使用配置的方式对资源进行权限控制。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {"/user/login" ).anonymous()"/testCors" ).hasAuthority("system:dept:list222" )
CSRF CSRF 是指跨站请求伪造(Cross-site request forgery),是 web 常见的攻击之一。
https://blog.csdn.net/freeking101/article/details/86537087
SpringSecurity 去防止 CSRF 攻击的方式就是通过 csrf_token。后端会生成一个 csrf_token,前端发起请求的时候需要携带这个 csrf_token, 后端会有过滤器进行校验,如果没有携带或者是伪造的就不允许访问。
我们可以发现 CSRF 攻击依靠的是 cookie 中所携带的认证信息。但是在前后端分离的项目中我们的认证信息其实是 token,而 token 并不是存储中 cookie 中,并且需要前端代码去把 token 设置到请求头中才可以,所以 CSRF 攻击也就不用担心了。
认证成功处理器 实际上在 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 进行登录认证的时候,如果登录成功了是会调用 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 的方法进行认证成功后的处理的。AuthenticationSuccessHandler 就是登录成功处理器。
我们也可以自己去自定义成功处理器进行成功后的相应处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Component public class SGSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {@Override public void onAuthenticationSuccess (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {"认证成功了" );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Autowired private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler;@Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
认证失败处理器 实际上在 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 进行登录认证的时候,如果认证失败了是会调用 AuthenticationFailureHandler 的方法进行认证失败后的处理的。AuthenticationFailureHandler 就是登录失败处理器。
我们也可以自己去自定义失败处理器进行失败后的相应处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Component public class SGFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {@Override public void onAuthenticationFailure (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {"认证失败了" );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Autowired private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler;@Autowired private AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler;@Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
登出成功处理器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Component public class SGLogoutSuccessHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler {@Override public void onLogoutSuccess (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {"注销成功" );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Autowired private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler;@Autowired private AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler;@Autowired private LogoutSuccessHandler logoutSuccessHandler;@Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {